Need help finding instrument?
We will gladly assist you in making the right decision to achieve your business goals
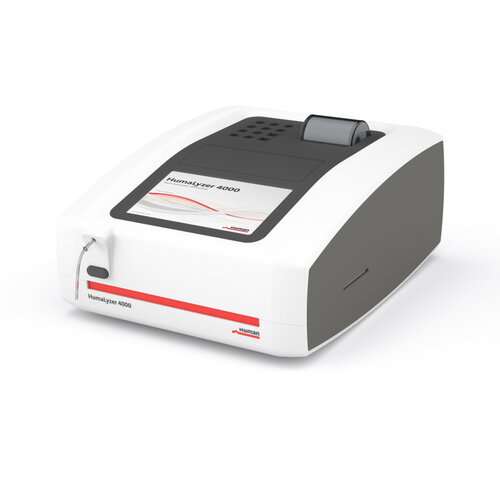


Price per unit:
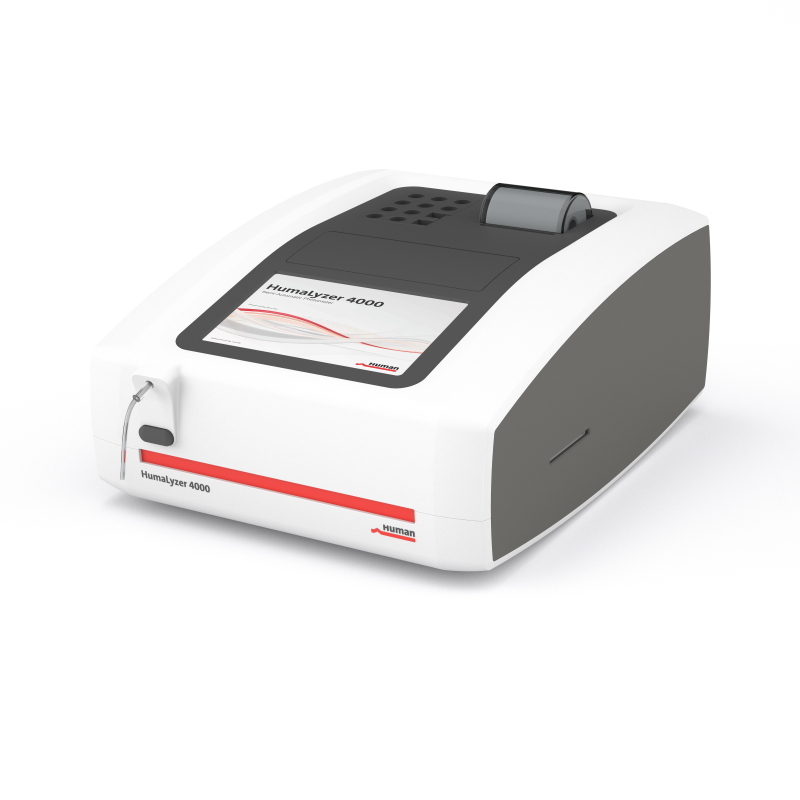
A pioneer in the field of clinical chemistry photometers
Wavelengths: 8
Integrated incubator
Color touchscreen
5W reflector lamp
Comprehensive assay selection “Made in Germany”
Open channels
Multi-language
Intuitive and powerful software
Efficient data management





Analyzer type
Reagent system
Reaction system
Analysis modes
Measuring modes
Reference channel optics
Liquid handling
QC module
LIS
Physical dimensions (W x D x H)
Environmental
















Flyer HumaLyzer 4000 EN
Flyer Clinical Chemistry Line EN
Flyer Clinical Chemistry Line ES
Flyer Clinical Chemistry Line FR
Flyer HumaLyzer 4000 ES
Flyer HumaLyzer 4000 FR
We will gladly assist you in making the right decision to achieve your business goals


